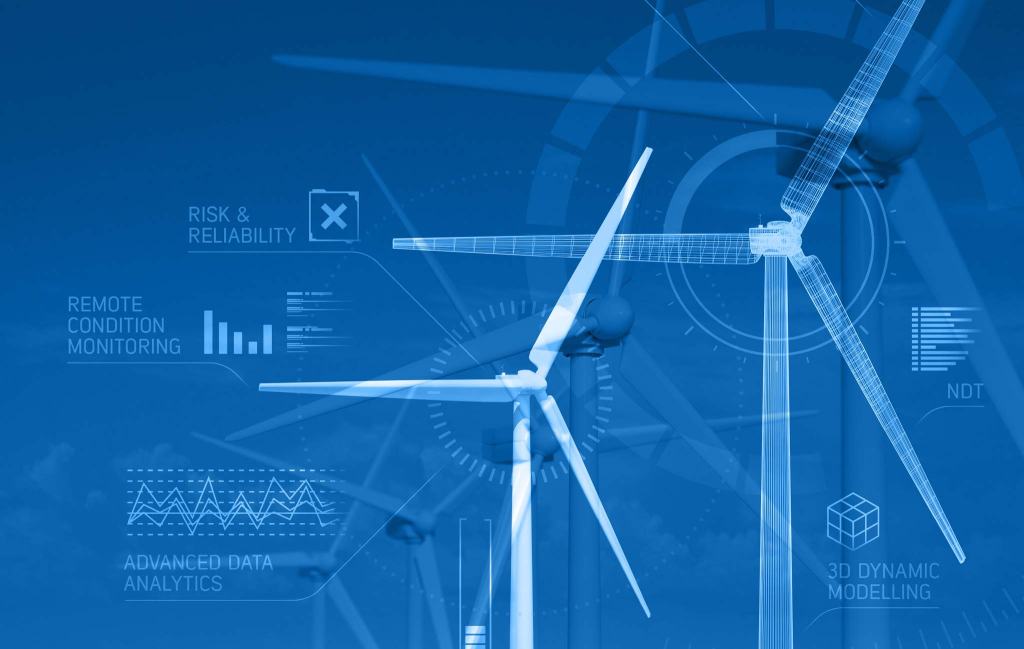
Digital twinning refers to the concept of creating a virtual replica or model of a physical object or system, with the aim of improving its performance, monitoring its status and predicting future behavior. It typically involves collecting data from sensors, simulating the object or system in a digital environment and using artificial intelligence and other technologies to analyze and understand its behavior. Digital twinning is commonly used in the Internet of Things (IoT), manufacturing, and industrial sectors, among others.
Digital twinning can be leveraged to build various services across different industries. Some examples include:
- Predictive Maintenance: In manufacturing, digital twinning can be used to model and monitor the performance of equipment and predict when maintenance is needed, based on real-time data from sensors.
- Supply Chain Management: In logistics and supply chain management, digital twinning can be used to create a virtual model of the supply chain network and monitor its performance, identifying bottlenecks, optimizing routes, and reducing costs.
- Smart Buildings: In the real estate industry, digital twinning can be used to create virtual models of buildings, monitor and optimize building performance, energy consumption, and comfort levels for occupants.
- Healthcare: In the healthcare industry, digital twinning can be used to model and monitor patients, predict potential health risks and improve patient outcomes.
- Remote Operations: Digital twinning can also be used to remotely monitor and control physical systems, such as machinery and vehicles, improving efficiency, reducing costs and minimizing the risk of human error.
The Metaverse and Digital Twins
Digital twinning is being used in the development of metaverse, which is a virtual world or collective space where users can interact and engage with each other and with virtual objects and environments. In the metaverse, digital twinning is used to create virtual representations of physical objects, systems, and even entire environments. These virtual twins can be used for various purposes such as simulation, visualization, and control, and can be connected to the physical world through various means, including sensors and actuators. The idea is to create a seamless, immersive experience between the physical and virtual worlds, where digital twins can provide valuable insights and information to help improve the real-world counterpart.
Digital twinning is being used in the metaverse in several ways:
- Virtual Object Representation: Digital twinning is used to create virtual representations of physical objects, such as furniture, vehicles, and other items that can be used in the metaverse. These virtual twins can be designed to closely resemble their physical counterparts and can be used to interact with the environment and other objects within the metaverse.
- Environment Simulation: Digital twinning is also being used to create virtual models of physical environments, such as cities, parks, and other public spaces. These virtual environments can be used to simulate and understand how real-world environments might behave, for example, predicting traffic patterns, energy consumption, and more.
- User Experience: Digital twinning is also being used to model and analyze user behavior within the metaverse. This can help metaverse developers understand how users interact with virtual environments and objects and optimize the user experience.
- Remote Operations: Digital twinning can also be used to remotely monitor and control virtual objects and environments within the metaverse, allowing metaverse developers to manage and update these elements without the need for manual intervention.
These are some of the ways digital twinning is being used in the metaverse, and it’s likely that this technology will play an even bigger role as the metaverse continues to evolve and grow.
The Benefits of Digital Twinning
Digital twinning has the potential to bring significant benefits to organizations in terms of cost savings and revenue generation. Some of the ways digital twinning can achieve this include:
- Predictive Maintenance: By modeling and monitoring physical systems, digital twinning can help organizations predict when maintenance is needed and schedule it in advance, reducing the risk of unplanned downtime and the associated costs.
- Improved Efficiency: Digital twinning can help organizations optimize their processes and systems, reducing waste and increasing efficiency, which can lead to cost savings and improved profitability.
- Better Decision Making: Digital twinning provides valuable insights into the performance of physical systems, which can be used to inform decision making and improve overall operational performance.
- New Revenue Streams: Digital twinning can also create new revenue streams by enabling organizations to offer value-added services such as remote monitoring and control, predictive maintenance, and more.
- Reduced Risk: Digital twinning can help organizations reduce risk by providing early warning of potential problems and enabling organizations to take proactive measures to prevent them.
These are just a few examples of how digital twinning can bring benefits to organizations. By creating a virtual replica of physical systems, digital twinning provides organizations with a powerful tool for improving performance, reducing costs, and generating new revenue streams.
Digital Twinning Software Tools
There are several software tools that can be used to create digital twins, including:
- Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms: IIoT platforms such as GE Predix, PTC ThingWorx, and Siemens MindSphere provide tools for collecting data from sensors and other sources, and for creating digital twins.
- Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software: CAD software such as Autodesk AutoCAD, Dassault Systemes CATIA, and Siemens NX can be used to create virtual representations of physical objects and systems.
- Simulation and modeling software: Tools such as ANSYS, Dassault Systemes SIMULIA, and PTC Creo can be used to simulate and model physical systems and their behavior.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) platforms: AI and ML platforms such as TensorFlow, Amazon SageMaker, and Microsoft Azure Machine Learning can be used to analyze and understand data from digital twins, and to make predictions about their future behavior.
- Geographic Information Systems (GIS) software: GIS software such as ESRI ArcGIS and QGIS can be used to create digital twins of physical environments and to visualize and analyze spatial data.
These are just a few examples, and the choice of software will depend on the specific needs and requirements of the digital twinning project. In some cases, multiple software tools may be combined to create a complete digital twinning solution.
Types of Digital Twin
There are several different types of digital twins, including:
- Physical Object Twin: A digital twin that represents a specific physical object, such as a machine, component, or product. This type of digital twin provides a virtual representation of the physical object and its behavior over time.
- Process Twin: A digital twin that represents a specific business process, such as a supply chain, production line, or logistics operation. This type of digital twin provides a virtual representation of the process and its interactions with other systems and processes.
- System Twin: A digital twin that represents a complete system, such as a building, factory, or power plant. This type of digital twin provides a virtual representation of the entire system and its components, and enables organizations to understand the system’s behavior and performance.
- Environmental Twin: A digital twin that represents a physical environment, such as a city, park, or natural environment. This type of digital twin provides a virtual representation of the environment and its behavior, and enables organizations to understand and manage the impact of human activities on the environment.
- User Twin: A digital twin that represents a specific user, such as a customer, employee, or citizen. This type of digital twin provides a virtual representation of the user’s behavior and preferences, and enables organizations to understand and anticipate their needs and wants.
These are some of the main types of digital twins, and there may be other variations and combinations depending on the specific needs and requirements of the organization. The type of digital twin used will depend on the specific goals and objectives of the project and the data and systems being modelled.
Creating Digital Twins
Creating a digital twin involves several steps, including:
- Define the objectives: Clearly define the goals and objectives of the digital twin project, such as improving efficiency, reducing downtime, or providing new insights into physical systems.
- Choose the right platform: Select a suitable platform for creating the digital twin, such as an IIoT platform, CAD software, simulation tool, or AI/ML platform.
- Gather data: Collect data from physical systems, sensors, and other sources to feed into the digital twin. This data can be used to create a virtual representation of the physical system and its behavior.
- Model the system: Use the data and software tools to create a virtual model of the physical system. This can involve creating a detailed representation of the system’s components, behavior, and interactions with other systems and processes.
- Validate the model: Validate the model by comparing its behavior with real-world data, and make any necessary adjustments to improve accuracy.
- Monitor and analyze data: Continuously monitor the physical system and the data fed into the digital twin, and use this data to analyze the system’s behavior and make predictions about its future performance.
- Update and refine the model: Regularly update and refine the digital twin as new data becomes available and new insights are gained, to keep the model accurate and up-to-date.
These steps provide a high-level overview of the process of creating a digital twin. The specific details and requirements will depend on the nature of the physical system being modeled and the goals of the project. It is also important to consider issues such as data privacy, security, and compliance when creating a digital twin.